For many Southern California homeowners, the monthly electric bill feels like a mystery. With confusing generation charges, delivery fees, and time-of-use rates, it’s easy to wonder exactly where your money goes. Whether you get your electricity from Southern California Edison (SCE), San Diego Gas & Electric (SDG&E), or the Los Angeles Department of Water and Power (LADWP), learning to read your bill is the key. It helps you understand your energy use and uncover ways to save, especially if you’re considering solar.
1. Start with the Account Summary
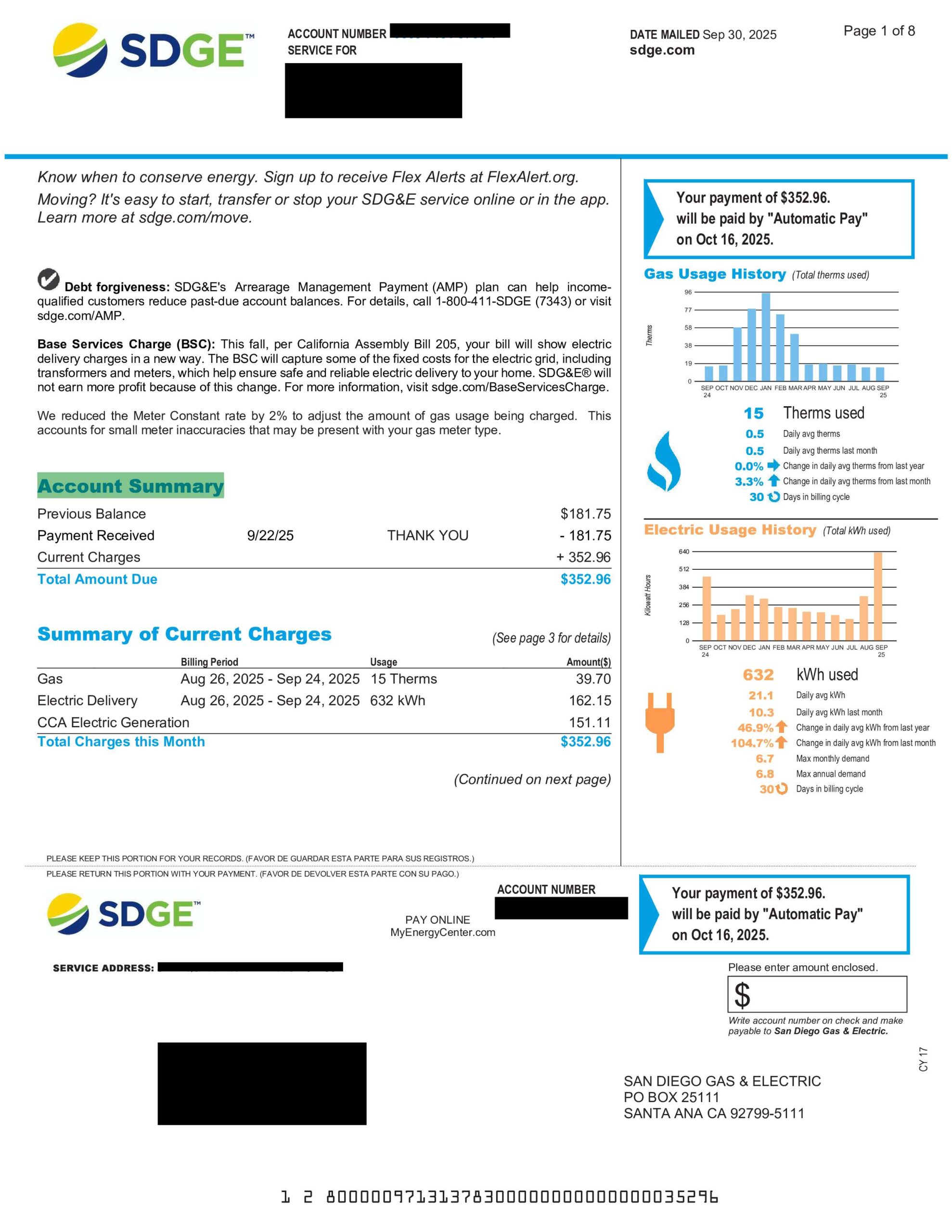
Your Account Summary provides a snapshot of your total balance, recent payments, and new charges for the billing period.
-
- SCE Example: At the top of page one, SCE lists your Amount Due and Due Date, followed by a breakdown that includes your previous balance, payment received, and new charges. You may also see messages such as “You Received a California Climate Credit”, which refers to a twice-yearly rebate from the state’s Cap-and-Trade program.
- SDG&E Example: The account summary shows your previous balance, recent payment, and new charges, with electric delivery, gas, and community energy generation listed separately. The payment due is the gas and electricity charges combined.
- LADWP Example: LADWP combines electricity, water, and sanitation into a single summary. You will see each service listed with its own subtotal and a total amount due at the bottom.
2. Understanding Energy Usage
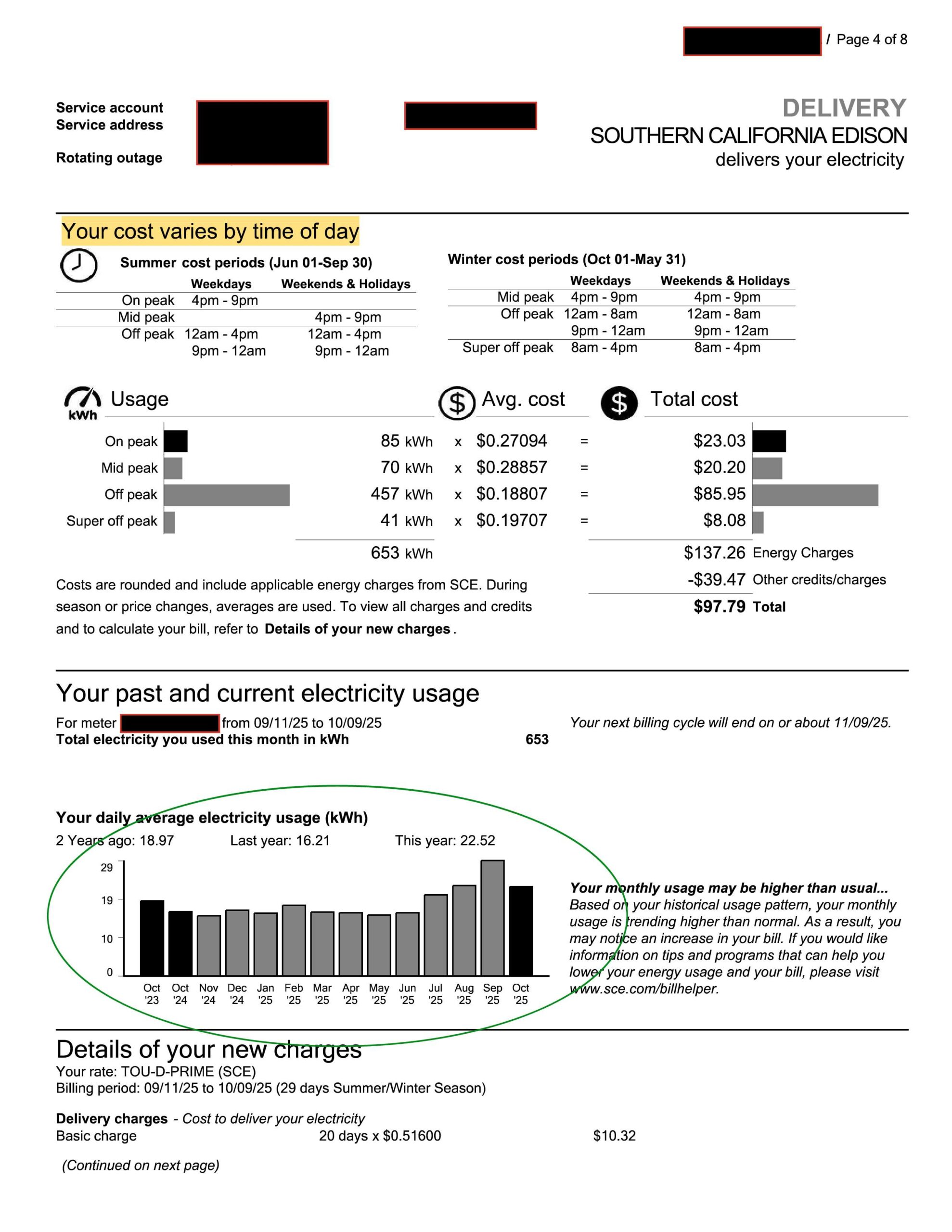
Your usage chart shows how much energy you use and when you use it.
-
- SCE: On page four, SCE displays a 12-month usage chart showing total kilowatt-hours (kWh) used and your daily average. This visual helps you easily spot seasonal spikes or patterns in your energy habits.
- SDG&E: The first page of the bill includes graphs for both Electric Usage History and Gas Usage History, showing monthly totals and year-over-year changes.
- LADWP: The Electric Charges page (typically page 3) shows how many kWh you used during the billing cycle and includes a bar graph comparing your recent months of use.
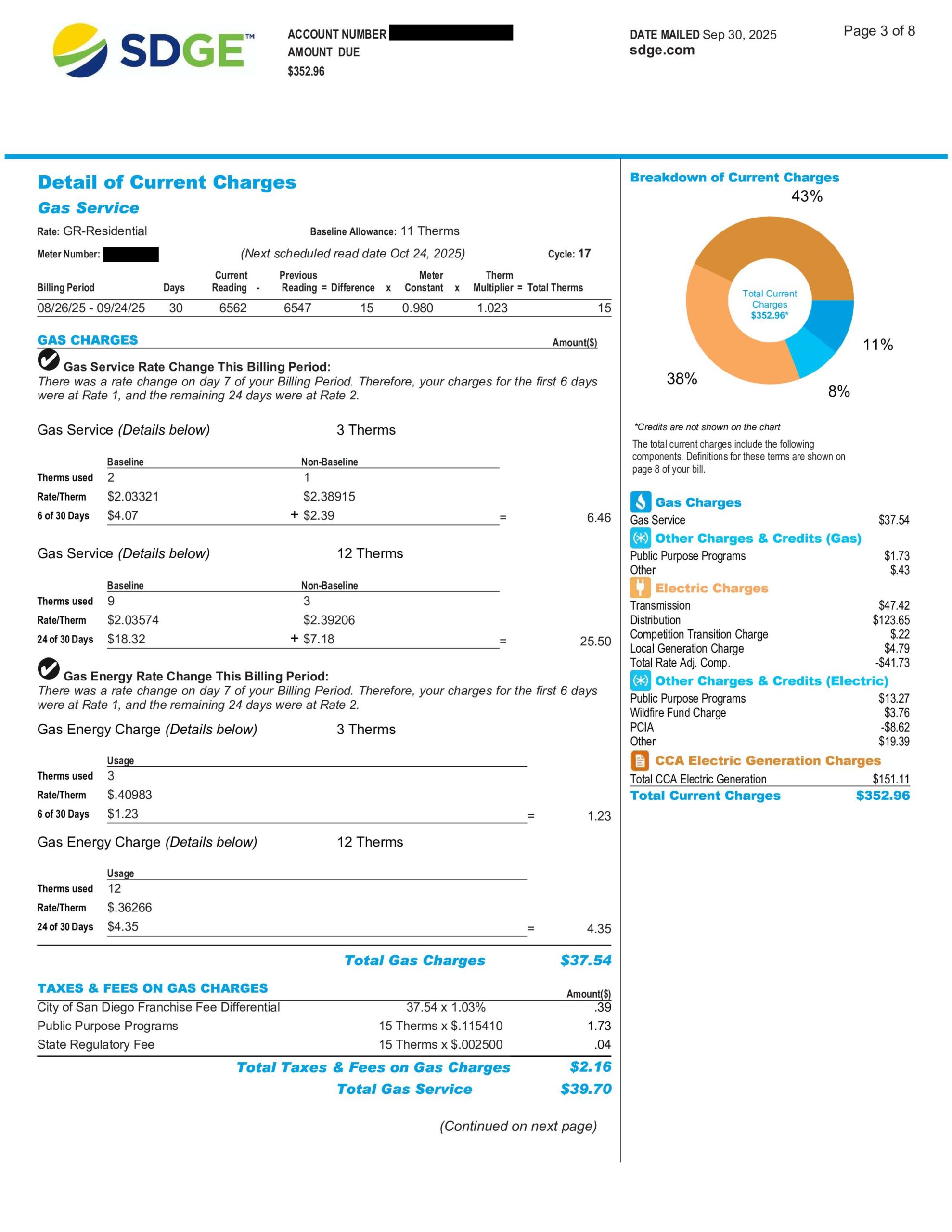
3. Breaking Down the Charges
This is often the most confusing part of any utility bill. To make it clear, each company divides your total into detailed sections that explain exactly what you are paying for.
Southern California Edison (SCE)
SCE separates its costs into two main categories:
-
- Delivery Charges: Covers the cost of bringing electricity to your home, including power line maintenance, grid operations, and customer service.
- Generation Charges: Reflects the cost of producing the electricity you use.
- Credits & Taxes: You may see the California Climate Credit twice a year and a small Utility User Tax imposed by some cities to fund municipal services.
San Diego Gas & Electric (SDG&E)
SDG&E provides detailed breakdowns for both gas and electricity charges:
-
- Electric Delivery: This covers the cost of maintaining the poles, wires, and meters that physically bring power to your home.
- Electric Generation: This section reflects the cost of creating or purchasing that power, often from providers like San Diego Community Power.
- Key Adjustments: Additional line items include wildfire prevention funds, Public Purpose Programs, and adjustments like the Power Charge Indifference Adjustment (PCIA).
Los Angeles Department of Water and Power (LADWP)
LADWP is unique as it combines electricity, water, and sanitation into a single bill. For electricity:
-
- Tiered Pricing Structure: LADWP uses tiered pricing, meaning the rate becomes progressively higher the more energy you use. This structure encourages conservation.
- Power Access Charge: This charge helps maintain the city’s electrical grid and customer service operations.
- Surcharges: The bill also includes small city and state surcharges that support renewable energy and infrastructure upkeep.
4. Rate Plans and Time-of-Use (TOU) Pricing
California utilities predominantly use Time-of-Use (TOU) or tiered pricing, which means the cost of electricity changes based on when you use it, with rates climbing higher during peak-demand hours.
-
- SCE: Page four includes a rate schedule showing on-peak, mid-peak, off-peak, and super off-peak hours.
- SDG&E: Offers plans like “DR-Residential” or “TOU-DR1,” where rates are highest between 4 p.m. and 9 p.m.
- LADWP: Uses a tier structure system where higher usage levels are billed at higher rates.
5. Taxes, Fees, and Adjustments
Every bill includes small charges that support state and local programs. Common examples include:
-
- Public Purpose Programs: Fund energy efficiency and low-income assistance.
- Wildfire Fund Charges: Help pay for prevention and recovery costs.
- Utility User Tax: City-imposed tax that varies by location.
- PCIA (Power Charge Indifference Adjustment): Ensures fair cost sharing between customers on different energy providers.
6. For Solar Homeowners: Tracking Energy Credits
If you already have solar panels, you need to track your performance using the Net Energy Metering (NEM) or Energy Credits section. Tracking these numbers helps ensure your solar system is performing as expected and that your credits are applied correctly
-
- SCE: Displays how much energy you sent to and received from the grid.
- SDG&E: Shows monthly credits and a “True-Up” at the end of each 12-month cycle.
- LADWP: Lists “Energy Credits” that carry over to offset future bills.
Tracking these numbers helps ensure your solar system is performing as expected and that your credits are applied correctly.
Final Thoughts
Understanding your utility bill is the first step toward gaining control over your energy costs. Once you know what each section means, you can easily spot usage patterns, reduce expenses by avoiding peak-hour costs, and explore solutions like solar or battery storage to lower your overall monthly payments.
If you are ready to see how much you can save, OC Solar can help. Our team will review your current bill, explain where your energy dollars are going, and design a solar system tailored to your home.
Visit OCSolar.com or call 949-427-8817 to schedule your free energy bill review today.